From Detectable Materials to Applications – Explore with GTRIC
Capacitive proximity sensors are quiet workhorses of automation. From liquid level monitoring to object detection on conveyors, they power countless industrial applications with precision and reliability. If you work in packaging, food processing, plastics, or logistics, understanding how these sensors operate—and what they can detect—can help you make smarter equipment choices and improve operational efficiency.
Let’s break it all down.
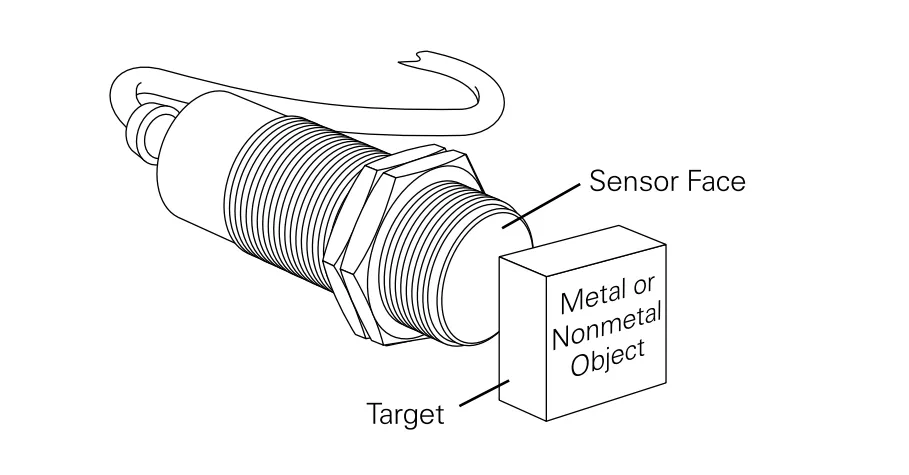
What is a Capacitive Proximity Sensor?
A capacitive proximity sensor is a non-contact device that detects a wide range of materials—including solids, liquids, and powders—without needing physical contact. Unlike inductive sensors, which are limited to metal targets, capacitive sensors detect virtually any material with a dielectric constant higher than air.
They’re commonly used in industrial environments to automate detection tasks, reduce mechanical wear, and enhance system responsiveness.
Why does this matter?
Because capacitive sensors don’t rely on contact, they work in places where touching a target could cause damage, contamination, or machine slowdown. That makes them essential in cleanrooms, food production, and high-speed systems.
How Does a Capacitive Proximity Sensors Work?
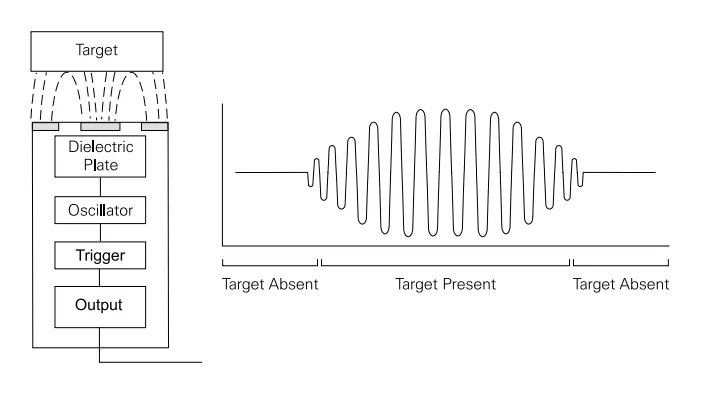
At their core, capacitive sensors work by sensing when something enters their electric field, triggering detection as the object’s charge-storing capacity alters the field. Here’s how it works:
- The sensor includes two electrodes that form a capacitor.
- When no object is nearby, the electric field remains stable.
- When an object enters the field, the dielectric properties of that object alter the capacitance.
- The sensor detects this change and switches its output accordingly.
Think of it like a touchless switch. The sensor doesn’t need to “see” the object—it senses the object’s electrical influence on its surrounding field.
Metaphor in Action:
Imagine standing near a radio antenna. You don’t touch it, but your body still interferes with the signal. Capacitive sensors operate on a similar principle—detecting disruption without physical interaction.
What is the Detection Range of a Capacitive Proximity Sensor?
Capacitive sensors typically offer short-range detection, but this is often all that’s needed for precise operations.
Typical Detection Distances:
- Standard models: 1 mm to 25 mm
- Extended-range models: Up to 60 mm or more (using larger or shielded sensors)
Detection Range Depends On:
- Field disturbance intensity correlates directly with target dimensions.
- Material type: Materials with higher dielectric constants (like water or glass) are easier to detect at a distance.
- Sensor size/design: Larger sensors or sensors with built-in amplifiers can offer greater range.
Note: Detection range isn’t fixed—it can be adjusted through sensor tuning (e.g., via potentiometers or digital settings), making it easy to fine-tune for your application.
Which of the Following Materials Can Be Detected by a Capacitive Proximity Detector?
Capacitive sensors can detect most materials, including non-metallic and metallic objects. Their detection capability is largely influenced by the target material’s dielectric constant.
| Material | Detected? | Why It Matters |
| Plastic | Yes | Ideal for packaging lines |
| Glass | Yes | Easily detected; used in bottling plants |
| Wood | Yes | Common in furniture and sawmill automation |
| Water | Yes | High dielectric; easy to detect |
| Metal | Yes | Detected, but inductive sensors may be better for metals |
| Paper | Yes | Useful in textile and printing lines |
| Air | No | Used as the baseline dielectric reference |
Practical Tip:
Capacitive sensors can even detect materials through non-conductive surfaces such as plastic, cardboard, or glass. For example, you can monitor liquid levels inside a sealed plastic container—no direct contact needed.
What are the strengths and weaknesses of capacitive proximity sensors?
Understanding the strengths and trade-offs of capacitive sensors can help you decide if they’re right for your setup.
Advantages:
- It can detect virtually any material, including solids, powders, and liquids.
- Non-contact operation reduces mechanical wear
- Capable of sensing through packaging or barriers
- Compact and versatile for tight installation spaces
- Resistant to vibration, dust, and light splashes
Disadvantages:
- Shorter sensing range than ultrasonic or photoelectric sensors
- Prone to false triggers due to environmental factors like humidity, temperature, or dust accumulation.
- May require frequent calibration in changing environments
- External objects in the vicinity can disrupt operation if shielding or tuning isn’t optimized.
Areas of Application of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors are used across industries for monitoring, detection, and feedback control. Their versatility makes them ideal for both standard and niche applications.
1. Food and Beverage Industry
- Detect presence of packaging material
- Measure liquid levels inside sealed containers
- Monitor cap application or fill height on bottling lines
Case Example:
A dairy plant uses capacitive sensors to detect milk levels in opaque plastic bottles, ensuring consistent fills without opening the packaging.
2. Agriculture
- Detect seed or fertilizer levels in hoppers
- Measure moisture content in grain silos
- Monitor water levels in irrigation systems
Application Tip: Capacitive sensors can alert farmers before a silo empties, reducing downtime and crop waste.
3. Plastics and Rubber Manufacturing
- Detect raw plastic pellets in feeders
- Sense plastic sheet position before cutting
- Monitor molded part presence in machines
4. Textile and Printing Industries
- Monitor the position of fabric rolls
- Detect thread tension or breaks
- Ensure correct alignment of paper sheets
5. Logistics and Packaging
- Detect items on conveyors
- Monitor fill levels in cartons or bins
Trigger label application when a box is in place
